Ectopic Pregnancy: What You Need to Know
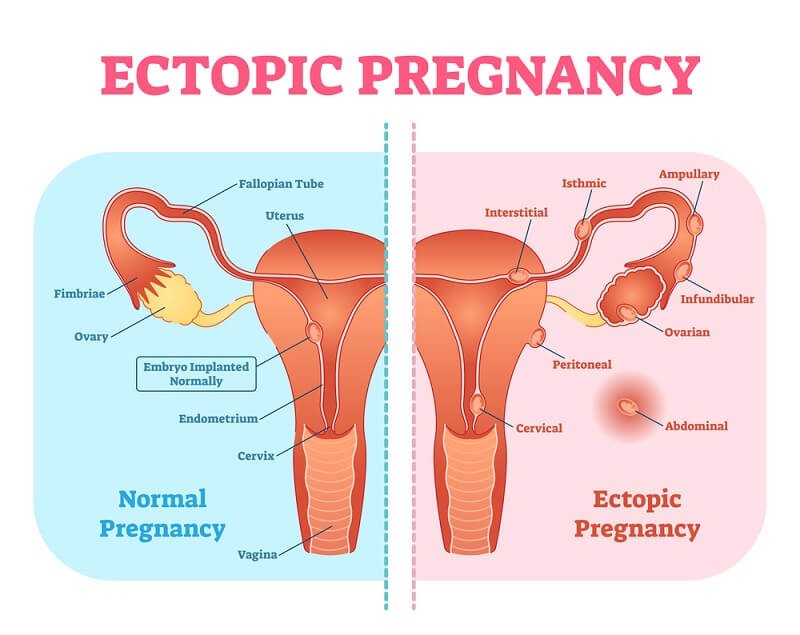
Pregnancy typically begins when a fertilized egg attaches to the lining of the uterus. However, in an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg implants and grows outside the main cavity of the uterus, often in a fallopian tube. This is known as a tubal pregnancy. In rare cases, an ectopic pregnancy can occur in other areas, such as the ovary, abdominal cavity, or cervix.
An ectopic pregnancy cannot proceed normally and can be life-threatening if left untreated. The fertilized egg cannot survive, and the growing tissue may cause severe bleeding.
In a healthy pregnancy, the fertilized egg attaches to the lining of the uterus. In contrast, an ectopic pregnancy occurs when the egg attaches outside the uterus, usually to the inside of a fallopian tube.
Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy may not be apparent at first, but some women may experience typical early signs of pregnancy, such as a missed period, breast tenderness, and nausea. However, as the fertilized egg grows in the improper place, symptoms become more noticeable.
Early warning signs of an ectopic pregnancy often include light vaginal bleeding and pelvic pain. If blood leaks from the fallopian tube, shoulder pain or an urge to have a bowel movement may occur. The specific symptoms depend on where the blood collects and which nerves are irritated.
If the fertilized egg continues to grow in the fallopian tube, it can cause the tube to rupture, leading to heavy bleeding inside the abdomen. Symptoms of this life-threatening event include extreme lightheadedness, fainting, and shock.
It is essential to seek emergency medical help if you experience any signs or symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy, including:
– Severe abdominal or pelvic pain accompanied by vaginal bleeding
– Extreme lightheadedness or fainting
– Shoulder pain
If you suspect you may have an ectopic pregnancy, do not delay seeking medical attention. Prompt treatment is crucial to prevent life-threatening complications.


